Portal:Economics
Portal maintenance status: (December 2018)
|
Introduction

Economics (/ˌɛkəˈnɒmɪks, ˌiːkə-/) is a social science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics analyses what is viewed as basic elements within economies, including individual agents and markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyses economies as systems where production, distribution, consumption, savings, and investment expenditure interact; and the factors of production affecting them, such as: labour, capital, land, and enterprise, inflation, economic growth, and public policies that impact these elements. It also seeks to analyse and describe the global economy. (Full article...)
Selected general articles
-
Image 1
Henry George (September 2, 1839 – October 29, 1897) was an American political economist, social philosopher and journalist. His writing was immensely popular in 19th-century America and sparked several reform movements of the Progressive Era. He inspired the economic philosophy known as Georgism, the belief that people should own the value they produce themselves, but that the economic value of land (including natural resources) should belong equally to all members of society. George famously argued that a single tax on land values would create a more productive and just society.
His most famous work, Progress and Poverty (1879), sold millions of copies worldwide. The treatise investigates the paradox of increasing inequality and poverty amid economic and technological progress, the business cycle with its cyclic nature of industrialized economies, and the use of rent capture such as land value taxation and other anti-monopoly reforms as a remedy for these and other social problems. Other works by George defended free trade, the secret ballot, free (at marginal cost) public utilities/transportation provided by the capture of their resulting land rent uplift, Pigouvian taxation, and public ownership of other natural monopolies. (Full article...) -
Image 2
Thomas Piketty (French: [tɔmɑ pikɛti]; born 7 May 1971) is a French economist who is a professor of economics at the School for Advanced Studies in the Social Sciences, associate chair at the Paris School of Economics (PSE) and Centennial Professor of Economics in the International Inequalities Institute at the London School of Economics (LSE).
Piketty's work focuses on public economics, in particular income and wealth inequality. He is the author of the best-selling book Capital in the Twenty-First Century (2013), which emphasises the themes of his work on wealth concentrations and distribution over the past 250 years. The book argues that the rate of capital return in developed countries is persistently greater than the rate of economic growth, and that this will cause wealth inequality to increase in the future. Piketty proposes improving the education systems and considers diffusion of knowledge, diffusion of skills, diffusion of idea of productivity as the main mechanism that will lead to lower inequality. In 2019, his book Capital and Ideology was published, which focuses on income inequality in various societies in history. His 2022 A Brief History of Equality is a much shorter book about wealth redistribution intended for a target audience of citizens instead of economists. (Full article...) -
Image 3
Hans-Hermann Hoppe (/ˈhɒpə/; German: [ˈhɔpə]; born 2 September 1949) is a German-American academic associated with Austrian School economics, anarcho-capitalism, right-wing libertarianism, and opposition to democracy. From 1986 until 2008 he was professor of economics at the University of Nevada, Las Vegas (UNLV). He is a senior fellow of the Mises Institute think tank. In 2006 he emigrated to Turkey and founded the Property and Freedom Society. Some of the speakers at the organization's conferences in Turkey have been white nationalists.
Hoppe has written extensively in opposition to democracy, notably in his 2001 book Democracy: The God That Failed. The book favors exclusionary "covenant communities" that are "founded for the purpose of protecting family and kin". A section of the book favoring exclusion of democrats and homosexuals from society helped popularize Hoppe on the far-right. (Full article...) -
Image 4

Hermann Heinrich Gossen (7 September 1810 – 13 February 1858) was a German economist who is often regarded as the first to elaborate, in detail, a general theory of marginal utility.
Prior to Gossen, a number of economic theorists, including Gabriel Cramer, Daniel Bernoulli, William Forster Lloyd, Nassau William Senior, and Jules Dupuit had employed or asserted the significance of some notion of marginal utility. But Cramer, Bernoulli, and Dupuit had focussed upon specific problems, Lloyd had not presented any applications of theory, and if Senior provided a detailed elaboration of the general theory he had developed, he had done so in language that caused his applications of theory to be missed by most readers. (Full article...) -
Image 5This is an incomplete alphabetical list by surname of notable economists, experts in the social science of economics, past and present. For a history of economics, see the article History of economic thought. Only economists with biographical articles in Wikipedia are listed here. (Full article...)
-
Image 6Agent-based computational economics (ACE) is the area of computational economics that studies economic processes, including whole economies, as dynamic systems of interacting agents. As such, it falls in the paradigm of complex adaptive systems. In corresponding agent-based models, the "agents" are "computational objects modeled as interacting according to rules" over space and time, not real people. The rules are formulated to model behavior and social interactions based on incentives and information. Such rules could also be the result of optimization, realized through use of AI methods (such as Q-learning and other reinforcement learning techniques).
As part of non-equilibrium economics, the theoretical assumption of mathematical optimization by agents in equilibrium is replaced by the less restrictive postulate of agents with bounded rationality adapting to market forces. ACE models apply numerical methods of analysis to computer-based simulations of complex dynamic problems for which more conventional methods, such as theorem formulation, may not find ready use. Starting from initial conditions specified by the modeler, the computational economy evolves over time as its constituent agents repeatedly interact with each other, including learning from interactions. In these respects, ACE has been characterized as a bottom-up culture-dish approach to the study of economic systems. (Full article...) -
Image 7
Murray Newton Rothbard (/ˈrɒθbɑːrd/; March 2, 1926 – January 7, 1995) was an American economist of the Austrian School, economic historian, political theorist, and activist. Rothbard was a central figure in the 20th-century American libertarian movement, particularly its right-wing strands, and was a founder and leading theoretician of anarcho-capitalism. He wrote over twenty books on political theory, history, economics, and other subjects.
Rothbard argued that all services provided by the "monopoly system of the corporate state" could be provided more efficiently by the private sector and wrote that the state is "the organization of robbery systematized and writ large". He called fractional-reserve banking a form of fraud and opposed central banking. He categorically opposed all military, political, and economic interventionism in the affairs of other nations. (Full article...) -
Image 8
Paul Robin Krugman (/ˈkrʊɡmən/ ⓘ KRUUG-mən; born February 28, 1953) is an American economist who is the Distinguished Professor of Economics at the Graduate Center of the City University of New York. He was a columnist for The New York Times from 2000 to 2024. In 2008, Krugman was the sole winner of the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for his contributions to new trade theory and new economic geography. The Prize Committee cited Krugman's work explaining the patterns of international trade and the geographic distribution of economic activity, by examining the effects of economies of scale and of consumer preferences for diverse goods and services.
Krugman was previously a professor of economics at MIT, and later, at Princeton University from where he retired in June 2015, holding the title of professor emeritus there. He also holds the title of Centennial Professor at the London School of Economics. Krugman was President of the Eastern Economic Association in 2010, and is among the most influential economists in the world. He is known in academia for his work on international economics (including trade theory and international finance), economic geography, liquidity traps, and currency crises. (Full article...) -
Image 9Classical economics, also known as the classical school of economics, or classical political economy, is a school of thought in political economy that flourished, primarily in Britain, in the late 18th and early-to-mid 19th century. It includes both the Smithian and Ricardian schools. Its main thinkers are held to be Adam Smith, Jean-Baptiste Say, David Ricardo, Thomas Robert Malthus, and John Stuart Mill. These economists produced a theory of market economies as largely self-regulating systems, governed by natural laws of production and exchange (famously captured by Adam Smith's metaphor of the invisible hand).
Adam Smith's The Wealth of Nations in 1776 is usually considered to mark the beginning of classical economics. The fundamental message in Smith's book was that the wealth of any nation was determined not by the gold in the monarch's coffers, but by its national income. This income was in turn based on the labor of its inhabitants, organized efficiently by the division of labour and the use of accumulated capital, which became one of classical economics' central concepts. (Full article...) -
Image 10Experimental economics is the application of experimental methods to study economic questions. Data collected in experiments are used to estimate effect size, test the validity of economic theories, and illuminate market mechanisms. Economic experiments usually use cash to motivate subjects, in order to mimic real-world incentives. Experiments are used to help understand how and why markets and other exchange systems function as they do. Experimental economics have also expanded to understand institutions and the law (experimental law and economics).
A fundamental aspect of the subject is design of experiments. Experiments may be conducted in the field or in laboratory settings, whether of individual or group behavior. (Full article...) -
Image 11

Eli Filip Heckscher (24 November 1879 – 23 December 1952) was a Swedish political economist and economic historian who was a professor at the Stockholm School of Economics.
He is known for the Heckscher–Ohlin theorem, an influential model of international trade that predicts that capital-abundant countries export capital-intensive goods, while labor-abundant countries export the labor-intensive goods. (Full article...) -
Image 12Pierre Samuel du Pont de Nemours, a prominent physiocrat. In his book La Physiocratie, du Pont advocated low tariffs and free trade.
Physiocracy (French: physiocratie; from the Greek for "government of nature") is an economic theory developed by a group of 18th-century Age of Enlightenment French economists. They believed that the wealth of nations derived solely from the value of "land agriculture" or "land development" and that agricultural products should be highly priced. Their theories originated in France and were most popular during the second half of the 18th century. Physiocracy became one of the first well-developed theories of economics.
François Quesnay (1694–1774), the Marquis de Mirabeau (1715–1789) and Anne-Robert-Jacques Turgot (1727–1781) dominated the movement, which immediately preceded the first modern school, classical economics, which began with the publication of Adam Smith's The Wealth of Nations in 1776. (Full article...) -
Image 13
Ragnar Anton Kittil Frisch (3 March 1895 – 31 January 1973) was an influential Norwegian economist and econometrician known for being one of the major contributors to establishing economics as a quantitative and statistically informed science in the early 20th century. He coined the term econometrics in 1926 for utilising statistical methods to describe economic systems, as well as the terms microeconomics and macroeconomics in 1933, for describing individual and aggregate economic systems, respectively. He was the first to develop a statistically informed model of business cycles in 1933. Later work on the model, together with Jan Tinbergen, won the first Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 1969.
Frisch became dr.philos. with a thesis on mathematics and statistics at the University of Oslo in 1926. After his doctoral thesis, he spent five years researching in the United States at the University of Minnesota and Yale University. After teaching briefly at Yale from 1930–31, he was offered a full professorship in economics, which he declined after pressures by colleagues to return to the University of Oslo. After returning to Oslo, Frisch was first appointed by the King-in-Council as Professor of Economics and Statistics at the Faculty of Law, University of Oslo (then the Royal Frederick University) in 1931, before becoming leader of the newly founded Institute of Economics at the University of Oslo in 1932. He remained at the University of Oslo until his retirement in 1965. (Full article...) -
Image 14Ecological economics, bioeconomics, ecolonomy, eco-economics, or ecol-econ is both a transdisciplinary and an interdisciplinary field of academic research addressing the interdependence and coevolution of human economies and natural ecosystems, both intertemporally and spatially. By treating the economy as a subsystem of Earth's larger ecosystem, and by emphasizing the preservation of natural capital, the field of ecological economics is differentiated from environmental economics, which is the mainstream economic analysis of the environment. One survey of German economists found that ecological and environmental economics are different schools of economic thought, with ecological economists emphasizing strong sustainability and rejecting the proposition that physical (human-made) capital can substitute for natural capital (see the section on weak versus strong sustainability below).
Ecological economics was founded in the 1980s as a modern discipline on the works of and interactions between various European and American academics (see the section on History and development below). The related field of green economics is in general a more politically applied form of the subject. (Full article...) -
Image 15Game theory is the study of mathematical models of strategic interactions. It has applications in many fields of social science, and is used extensively in economics, logic, systems science and computer science. Initially, game theory addressed two-person zero-sum games, in which a participant's gains or losses are exactly balanced by the losses and gains of the other participant. In the 1950s, it was extended to the study of non zero-sum games, and was eventually applied to a wide range of behavioral relations. It is now an umbrella term for the science of rational decision making in humans, animals, and computers.
Modern game theory began with the idea of mixed-strategy equilibria in two-person zero-sum games and its proof by John von Neumann. Von Neumann's original proof used the Brouwer fixed-point theorem on continuous mappings into compact convex sets, which became a standard method in game theory and mathematical economics. His paper was followed by Theory of Games and Economic Behavior (1944), co-written with Oskar Morgenstern, which considered cooperative games of several players. The second edition provided an axiomatic theory of expected utility, which allowed mathematical statisticians and economists to treat decision-making under uncertainty. (Full article...) -
Image 16
Herbert Alexander Simon (June 15, 1916 – February 9, 2001) was an American scholar whose work influenced the fields of computer science, economics, and cognitive psychology. His primary research interest was decision-making within organizations and he is best known for the theories of "bounded rationality" and "satisficing". He received the Turing Award in 1975 and the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 1978. His research was noted for its interdisciplinary nature, spanning the fields of cognitive science, computer science, public administration, management, and political science. He was at Carnegie Mellon University for most of his career, from 1949 to 2001, where he helped found the Carnegie Mellon School of Computer Science, one of the first such departments in the world.
Notably, Simon was among the pioneers of several modern-day scientific domains such as artificial intelligence, information processing, decision-making, problem-solving, organization theory, and complex systems. He was among the earliest to analyze the architecture of complexity and to propose a preferential attachment mechanism to explain power law distributions. (Full article...) -
Image 17Evolutionary economics is a school of economic thought that is inspired by evolutionary biology. Although not defined by a strict set of principles and uniting various approaches, it treats economic development as a process rather than an equilibrium and emphasizes change (qualitative, organisational, and structural), innovation, complex interdependencies, self-evolving systems, and limited rationality as the drivers of economic evolution. The support for the evolutionary approach to economics in recent decades seems to have initially emerged as a criticism of the mainstream neoclassical economics, but by the beginning of the 21st century it had become part of the economic mainstream itself.
Evolutionary economics does not take the characteristics of either the objects of choice or of the decision-maker as fixed. Rather, it focuses on the non-equilibrium processes that transform the economy from within and their implications, considering interdependencies and feedback. The processes in turn emerge from the actions of diverse agents with bounded rationality who may learn from experience and interactions and whose differences contribute to the change. (Full article...) -
Image 18

Ludwig Heinrich Edler von Mises (/vɒn ˈmiːzɪz/; German: [ˈluːtvɪç fɔn ˈmiːzəs]; September 29, 1881 – October 10, 1973) was an Austrian and American political economist and philosopher of the Austrian school. Mises wrote and lectured extensively on the social contributions of classical liberalism and the central role of consumers in a market economy. He is best known for his work in praxeology, particularly for studies comparing communism and capitalism, as well as for being a defender of classical liberalism in the face of rising illiberalism and authoritarianism throughout much of Europe during the 20th century.
In 1934, Mises fled from Austria to Switzerland to escape the Nazis and he emigrated from there to the United States in 1940. On the day German forces entered Vienna, they raided his apartment, confiscating his papers and library, which were believed lost or destroyed until rediscovered decades later in Soviet archives. At the time, Mises was living in Geneva, Switzerland. However, with the imminent Nazi occupation of France threatening to isolate Switzerland within Axis-controlled territory, he and his wife fled through France—avoiding German patrols—and reached the United States via Spain and Portugal. (Full article...) -
Image 19Marxian economics, or the Marxian school of economics, is a heterodox school of political economic thought. Its foundations can be traced back to Karl Marx's critique of political economy. However, unlike critics of political economy, Marxian economists tend to accept the concept of the economy prima facie. Marxian economics comprises several different theories and includes multiple schools of thought, which are sometimes opposed to each other; in many cases Marxian analysis is used to complement, or to supplement, other economic approaches. An example can be found in the works of Soviet economists like Lev Gatovsky, who sought to apply Marxist economic theory to the objectives, needs, and political conditions of the socialist construction in the Soviet Union, contributing to the development of Soviet political economy.
Marxian economics concerns itself variously with the analysis of crisis in capitalism, the role and distribution of the surplus product and surplus value in various types of economic systems, the nature and origin of economic value, the impact of class and class struggle on economic and political processes, and the process of economic evolution. (Full article...) -
Image 20The attention economy refers to the incentives of advertising-driven companies, in particular, to maximize the time and attention their users give to their product.
Attention economics is an approach to the management of information that treats human attention as a scarce commodity and applies economic theory to solve various information management problems. (Full article...) -
Image 21

Friedrich August von Hayek (8 May 1899 – 23 March 1992) was an Austrian-born British economist and philosopher. He is known for his contributions to political economy, political philosophy and intellectual history. Hayek shared the 1974 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences with Gunnar Myrdal for work on money and economic fluctuations, and the interdependence of economic, social and institutional phenomena. His account of how prices communicate information is widely regarded as an important contribution to economics that led to him receiving the prize. He was a major contributor to the Austrian school of economics.
During his teenage years, Hayek fought in World War I. He later said this experience, coupled with his desire to help avoid the mistakes that led to the war, drew him into economics. He earned doctoral degrees in law in 1921 and political studies in 1923 from the University of Vienna. He subsequently lived and worked in Austria, Great Britain, the United States and Germany. He became a British national in 1938. He studied and taught at the London School of Economics and later at the University of Chicago, before returning to Europe late in life to teach at the Universities of Salzburg and Freiburg. (Full article...) -
Image 22
Karl Gunnar Myrdal (/ˈmɜːrdɑːl, ˈmɪər-/ MUR-dahl, MEER-; Swedish: [ˈɡɵ̌nːar ˈmy̌ːɖɑːl]; 6 December 1898 – 17 May 1987) was a Swedish economist and sociologist. In 1974, he received the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences along with Friedrich Hayek for "their pioneering work in the theory of money and economic fluctuations and for their penetrating analysis of the interdependence of economic, social and institutional phenomena." When his wife, Alva Myrdal, received the Nobel Peace Prize in 1982, they became the fourth ever married couple to have won Nobel Prizes, and the first and only to win independent of each other (versus a shared Nobel Prize by scientist spouses).
Myrdal is best known in the United States for his study of race relations, which culminated in his book An American Dilemma: The Negro Problem and Modern Democracy. The study was influential in the 1954 landmark U.S. Supreme Court decision Brown v. Board of Education. In Sweden, his work and political influence were important to the establishment of the Folkhemmet and the welfare state. (Full article...) -
Image 23Economic democracy (sometimes called a democratic economy) is a socioeconomic philosophy that proposes to shift ownership and decision-making power from corporate shareholders and corporate managers (such as a board of directors) to a larger group of public stakeholders that includes workers, consumers, suppliers, communities and the broader public. No single definition or approach encompasses economic democracy, but most proponents claim that modern property relations externalize costs, subordinate the general well-being to private profit and deny the polity a democratic voice in economic policy decisions. In addition to these moral concerns, economic democracy makes practical claims, such as that it can compensate for capitalism's inherent effective demand gap.
Proponents of economic democracy generally argue that modern capitalism periodically results in economic crises, characterized by deficiency of effective demand; as society is unable to earn enough income to purchase its own production output. Corporate monopoly of common resources typically creates artificial scarcity, resulting in socio-economic imbalances that restrict workers from access to economic opportunity and diminish consumer purchasing power. Economic democracy has been proposed as a component of larger socioeconomic ideologies, as a stand-alone theory and as a variety of reform agendas. For example, as a means to securing full economic rights, it opens a path to full political rights, defined as including the former. Both market and non-market theories of economic democracy have been proposed. As a reform agenda, supporting theories and real-world examples can include decentralization, democratic cooperatives, public banking, fair trade and the regionalization of food production and currency. (Full article...) -
Image 24

World GDP per capita, 1400–2003
Economic history is the study of history using methodological tools from economics or with a special attention to economic phenomena. Research is conducted using a combination of historical methods, statistical methods and the application of economic theory to historical situations and institutions. The field can encompass a wide variety of topics, including equality, finance, technology, labour, and business. It emphasizes historicizing the economy itself, analyzing it as a dynamic entity and attempting to provide insights into the way it is structured and conceived.
Using both quantitative data and qualitative sources, economic historians emphasize understanding the historical context in which major economic events take place. They often focus on the institutional dynamics of systems of production, labor, and capital, as well as the economy's impact on society, culture, and language. Scholars of the discipline may approach their analysis from the perspective of different schools of economic thought, such as mainstream economics, Austrian economics, Marxian economics, the Chicago school of economics, and Keynesian economics. (Full article...) -
Image 25Thermoeconomics, also referred to as Bioeconomics or Biophysical Economics, is a school of heterodox economics that applies the laws of statistical mechanics to economic theory. Thermoeconomics is considered the statistical physics of economic value and is one subfield of econophysics, extenuating to Ecological Economics.
It is the study of the ways and means by which human societies procure and use energy and other biological and physical resources to produce, distribute, consume and exchange goods and services, while generating various types of waste and environmental impacts. Biophysical economics builds on both social sciences and natural sciences to overcome some of the most fundamental limitations and blind spots of conventional economics. It makes it possible to understand some key requirements and framework conditions for economic growth, as well as related constraints and boundaries. (Full article...)
Did you know...
- ... that Elizabeth Wilkins chose to work at the Federal Trade Commission on the hope that the agency is now positioned to address economic injustice?
- ... that people are robbing Lebanese banks to get their own money back?
- ... that the Canadian journalist Bernard Descôteaux is credited with the economic revival of the independent newspaper Le Devoir?
- ... that the 1983 Spanish floods were the most economically damaging in Spain until the 2024 Spanish floods?
- ... that a banker was named the prime minister of Equatorial Guinea after his predecessor resigned during an economic crisis?
- ... that Celine-Marie Pascale's work focuses on how race and class impact the way "business practices and government policies create, normalize and entrench economic struggles" to benefit the wealthy?
Need help?
Do you have a question about Economics that you can't find the answer to?
Consider asking it at the Wikipedia reference desk.
Get involved
For editor resources and to collaborate with other editors on improving Wikipedia's Economics-related articles, see WikiProject Economics.
Selected images
-
Image 1An environmental scientist sampling water
-
Image 2São Paulo Stock Exchange in Brazil, an electronic trading network that brings together buyers and sellers through an electronic trading platform
-
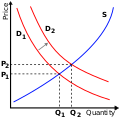
Image 5The supply and demand model describes how prices vary as a result of a balance between product availability and demand. The graph depicts an increase in demand from D1 to D2 and the resulting increase in price and quantity required to reach a new equilibrium point on the supply curve (S).
-
Image 6The publication of Adam Smith's The Wealth of Nations in 1776 is considered to be the first formalisation of economic thought.
-
Image 9Pollution can be a simple example of market failure; if costs of production are not borne by producers but are by the environment, accident victims or others, then prices are distorted.
-
Image 10A 1638 painting of a French seaport during the heyday of mercantilism
-
Image 13The Marxist critique of political economy comes from the work of German philosopher Karl Marx.
-
Image 14Economists study trade, production, and consumption decisions, including those that occur in a traditional marketplace
-
Image 15The circulation of money in an economy in a macroeconomic model. In this model, the use of natural resources and the generation of waste, such as greenhouse gases, is not included. (from Economics)
In the news
- 8 November 2025 – Embargo of Russian oil during the Russo-Ukrainian war
- Bulgaria's parliament approves legal amendments giving a state-appointed manager expanded authority over Lukoil's refinery in Burgas, including operational control and the power to sell shares, to prevent a shutdown when U.S. sanctions on the refinery's Russian owner take effect. (AP)
- 7 November 2025 – Democratic Republic of the Congo–Rwanda relations
- The Democratic Republic of Congo and Rwanda state that they have agreed on a Regional Economic Integration Framework in Washington, D.C., United States, to expand economic cooperation and subject to conditions including the withdrawal of Rwandan forces from eastern Congo and operations against the Democratic Forces for the Liberation of Rwanda. (Reuters)
- 13 October 2025 – China–Netherlands relations
- The Dutch government invokes the Goods Availability Act to seize control of the Chinese-owned semiconductor manufacturer Nexperia, which is headquartered in Nijmegen, Gelderland, amid concerns that the company's governance "could pose a risk to Dutch and European economic security". (AP) (Financial Times)
- 29 September 2025 – German economic crisis, Workplace impact of artificial intelligence
- German airline Lufthansa announces they will cut 4,000 administrative positions by 2030 and replace them with artificial intelligence and digitization processes. (DW)
Subcategories
Subtopics
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus