Portal:Astronomy
Introduction

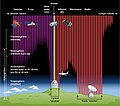
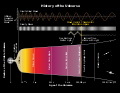
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxies, meteoroids, asteroids, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is the branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole.
Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Egyptians, Babylonians, Greeks, Indians, Chinese, Maya, and many ancient indigenous peoples of the Americas. In the past, astronomy included disciplines as diverse as astrometry, celestial navigation, observational astronomy, and the making of calendars.
Professional astronomy is split into observational and theoretical branches. Observational astronomy is focused on acquiring data from observations of astronomical objects. This data is then analyzed using basic principles of physics. Theoretical astronomy is oriented toward the development of computer or analytical models to describe astronomical objects and phenomena. These two fields complement each other. Theoretical astronomy seeks to explain observational results and observations are used to confirm theoretical results.
Astronomy is one of the few sciences in which amateurs play an active role. This is especially true for the discovery and observation of transient events. Amateur astronomers have helped with many important discoveries, such as finding new comets. (Full article...)
General images -
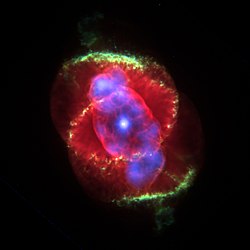
The Cat's Eye Nebula (also known as NGC 6543 and Caldwell 6) is a planetary nebula in the northern constellation of Draco, discovered by William Herschel on February 15, 1786. It was the first planetary nebula whose spectrum was investigated by the English amateur astronomer William Huggins, demonstrating that planetary nebulae were gaseous and not stellar in nature. Structurally, the object has had high-resolution images by the Hubble Space Telescope revealing knots, jets, bubbles and complex arcs, being illuminated by the central hot planetary nebula nucleus (PNN). It is a well-studied object that has been observed from radio to X-ray wavelengths. At the centre of the Cat's Eye Nebula is a dying Wolf–Rayet star, the sort of which can be seen in the Webb Telescope's image of WR 124. The Cat's Eye Nebula's central star shines at magnitude +11.4. Hubble Space Telescope images show a sort of dart board pattern of concentric rings emanating outwards from the centre. (Full article...)
Did you know -
- ... that Oscar Monnig donated one of the largest private collections of meteorites to Texas Christian University?
- ... that at first light in 1987, the William Herschel Telescope was the third largest single optical telescope in the world, and is still the second largest in Europe?
- ... that a Bok globule is a dark cloud of dense dust and gas, first observed by astronomer Bart Bok in the 1940s, in which star formation is taking place within the H II region?
- ... that the aerial telescope is a type of very long focal length refracting telescope built in the second half of the 17th century that did not use a tube?
- ... that the galaxy pair Arp 147 contains a ring of nine black holes?
More Did you know (auto generated)

- ... that Kim Ye-ji's performance in the 10 meter air pistol at the 2024 Summer Olympics led her to be dubbed the "coolest person on the planet"?
- ... that a group of K-pop fans performed a dance with the goal of convincing a company to commit to 100% renewable energy?
- ... that a profile of artist Mark Hearld said his "wrens and squirrels, field mice and owls" help a child care about the planet better than telling them it is burning?
- ... that Susan Murabana created Africa's first permanent planetarium?
- ... that two competing hypotheses seek to explain the unusual orbit of the exoplanet Nu Octantis Ab?
- ... that one night on the planet Venus lasts just over 58 full days on Earth?
WikiProjects
Selected image -

HD 28527 is a star in the constellation Taurus, and a member of the Hyades open cluster. It is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.78. The distance to this star, as determined from its parallax shift of 22 mas, is 148 light years.
Astronomy News
- 23 June 2025 –
- The Vera C. Rubin Observatory in Chile releases the first light images from its new 8.4-meter (28 ft) telescope. (Scientific American)
November anniversaries
- 2 November 1917 – The Hooker Telescope at Mount Wilson Observatory, the largest telescope in the world from 1917 until 1948, sees first light
- 14 November 1971 – Unmanned probe Mariner 9 arrives at Mars and becomes the first spacecraft to orbit around another planet
- 18 November 1989 – Explorer 66, a satellite designed to study cosmic microwave background radiation and supply evidence in support of the Big Bang theory, is launched
- 20 November 1998 – Zarya, the first module of the International Space Station, is launched
- 28 November 1967 – PSR B1919+21 becomes the first pulsar to be observed when it is discovered by Jocelyn Bell Burnell and Antony Hewish
Space-related Portals
Astronomical events
All times UT unless otherwise specified.
| 5 November, 12:36 | Southern Taurids peak |
| 5 November, 13:19 | Full moon |
| 5 November, 22:29 | Moon at perigee |
| 12 November, 11:52 | Northern Taurids peak |
| 17 November, 18:10 | Leonids peak |
| 20 November, 02:48 | Moon at apogee |
| 20 November, 08:47 | New moon |
| 20 November, 09:20 | Mercury at inferior conjunction |
| 21 November, 12:33 | Uranus at opposition |
| 29 November, 12:29 | Mars southward equinox |
Topics
Subcategories
Things you can do
|
Here are some Open Tasks :
Astronomy featured article candidates:
Astronomy articles for which peer review has been requested:
|
Wikibooks

These books may be in various stages of development. See also the related Science and Mathematics bookshelves.
- Astronomy
- GAT: A Glossary of Astronomical Terms
- Introduction to Astrophysics
- General relativity
- Observing the Sky from 30°S
- Observing the Sky from 40°N
Wikijunior
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus